Deploy Invicti Shark for Node.js - AWS Elastic Beanstalk
Invicti Shark enables you to carry out interactive security testing (IAST) in your web application to confirm more vulnerabilities and further minimize false positives.
- Node.js is an open source server environment designed to build scalable network applications, as it's capable of handling a vast number of simultaneous connections with high throughput. Depending on the specific frameworks and libraries, debugging a Node.js application can be tricky though.
- You can take advantage of Invicti's unique DAST-induced IAST approach to get an inside view into how security checks and test payloads are processed within these environments. These additional insights let you isolate the location and root cause of security defects quickly.
For more information, see Invicti adds IAST support for Node.js.
This document shows you how you can run a Node.js application in AWS Elastic Beanstalk and then use the Shark to run an interactive application security testing (IAST) scan for that application.
Step 1: Add your website to Invicti Enterprise
For this example, assume that the URL for your target is http://eb.acunetixexample.com.
- Add your website to Invicti. For more information, refer to the How to add a website in Invicti Enterprise document.
- Download the Node.js sensor. For more information, refer to the Downloading Shark sensors in Invicti Enterprise document.
- Save the Node.js sensor file to use it later on.
Step 2: Create your application source code bundle
This simple web application is defined through the following file structure:
~/axexample-nodejs/
~/axexample-nodejs/app.js
~/axexample-nodejs/package.json
~/axexample-nodejs/Shark (IAST and SCA).tar
- Create your
/axexample-nodejs/app.jsfile to read as follows:
const app = require('express')();
var port = process.env.PORT || 60000;
app.get('/', function (req, res) {
res.send(
'<html><body>' +
'<h1>Test Node.js Site Example for AWS Elastic Beanstalk</h1>' +
'<br>' +
'Hello World! - Main Page' +
'<br>' +
'<a href="/page1">Goto Page 1</a>' +
'</body></html>'
);
});
app.get('/page1', function (req, res) {
res.send(
'<html><body>' +
'<h1>Test Node.js Site Example for AWS Elastic Beanstalk</h1>' +
'<br>' +
'Hello World! - Page 1' +
'<br>' +
'<a href="/">Goto Main Page</a>' +
'</body></html>'
);
});
app.listen(port, function(err){
if (err) console.log(err);
console.log("Server listening on port: ", port);
});
- Create your
/axexample-nodejs/package.jsonfile to read as follows:
{
"name": "axexample-nodejs",
"version": "1.0.0",
"dependencies": {
"express": "*",
"node-acusensor": "file:Shark (IAST and SCA).tar"
},
"scripts": {
"start": "npx Shark (IAST and SCA).tar app.js"
}
}
- Copy the
Shark (IAST and SCA).tarfile you created earlier into~/axexample-nodejs/Shark (IAST and SCA).tar. - Finally, build the source code bundle with:
cd ~/axexample-nodejs
zip -rq axexample-nodejs.zip
- Download your
invicti-nodejs.zipfile to your desktop and retain your ZIP file for the following deployment steps.
Step 3: Deploy your web application to AWS elastic beanstalk
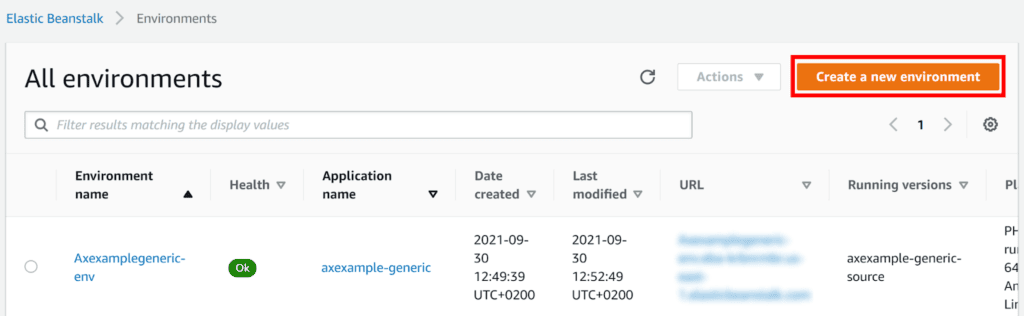
- From your AWS Dashboard, navigate to Elastic Beanstalk > Environments.
- Choose Create a new environment.
-
Set your environment tier to Web server environment.
-
Click Select.
-
On the Elastic Beanstalk > Create environment page:
-
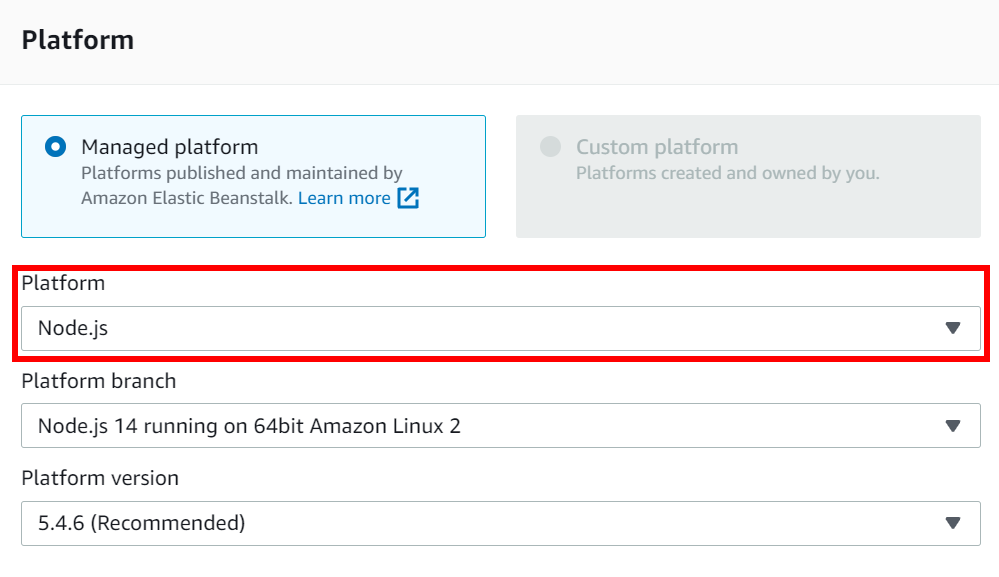
Set the Application name field to the name for your web application; for this example, use
axexample-nodejs. -
From the Platform drop-down, choose Node.js.
-
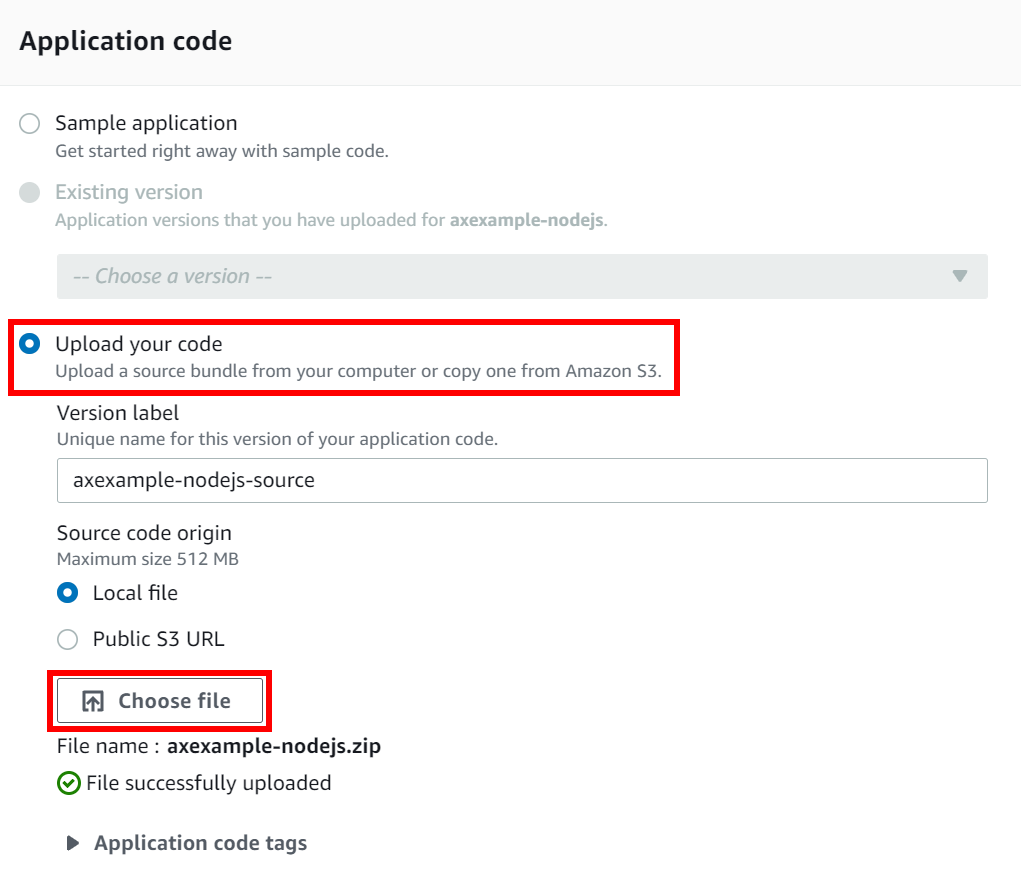
Enable the Upload your code option and choose Choose file.
-
Choose your
Node.js zipsource code bundle for upload and choose Create environment.
-
-
AWS Elastic Beanstalk creates your environment, and this can take a few minutes. When the process is complete, you're redirected to your environment's dashboard.
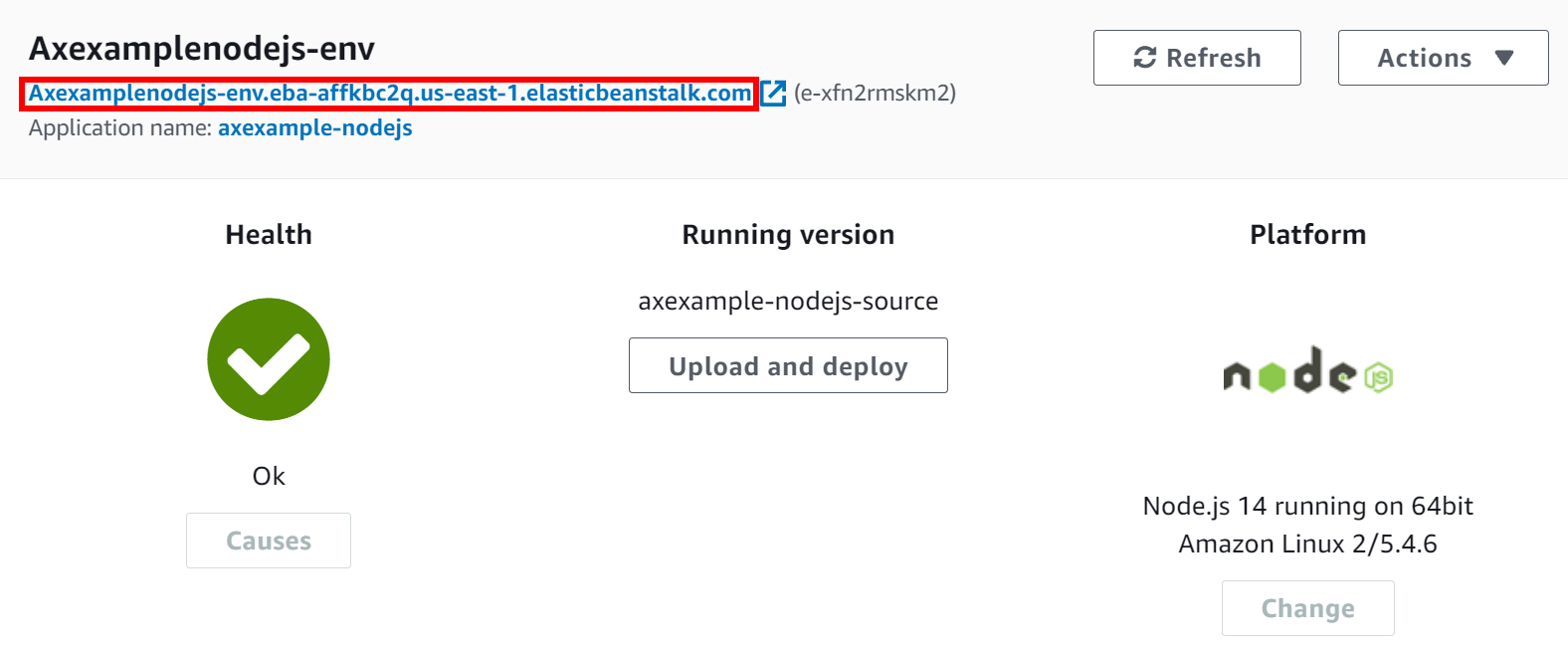
- Take note of your environment's new URL which was created automatically by AWS Elastic Beanstalk:
- You need this to create a CNAME to point to this URL.
- In this example, create a CNAME for
eb.acunetixexample.comto point toaxexamplenodejs-env.eba-affkbc2q.us-east-1.elasticbeanstalk.com; here is an example using the Namecheap cPanel interface:
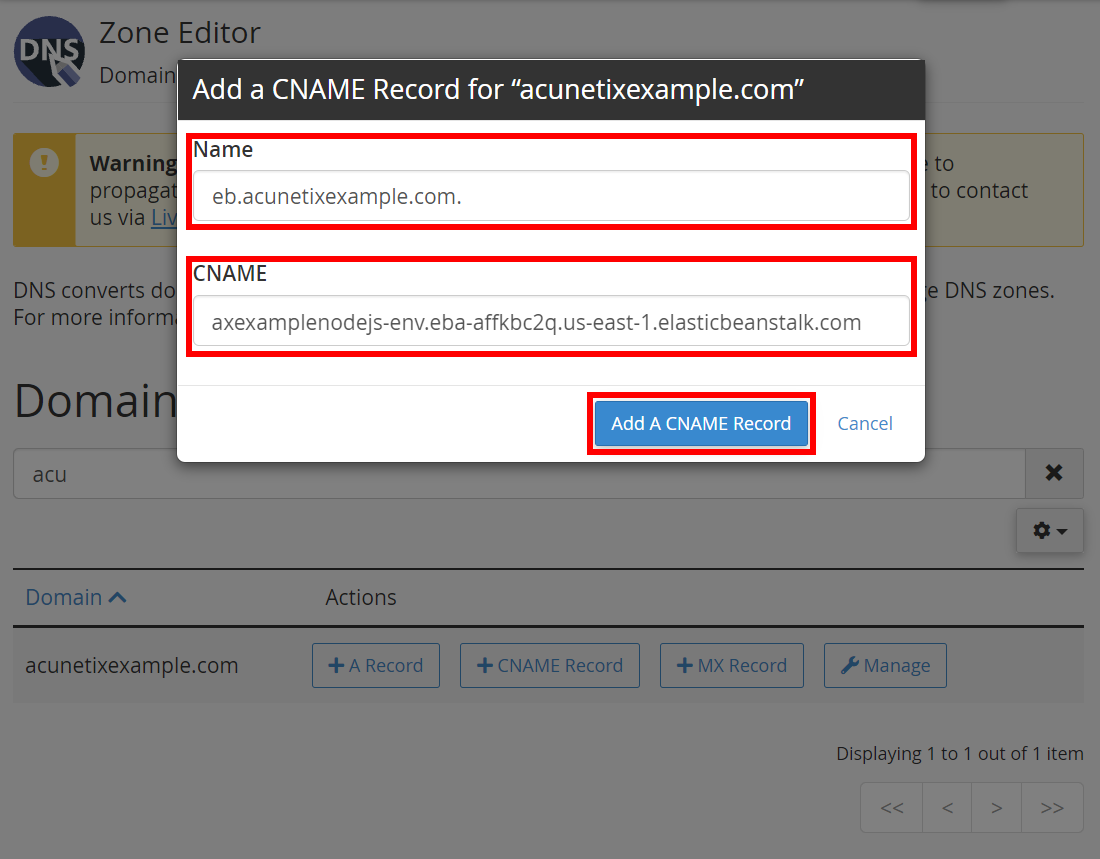
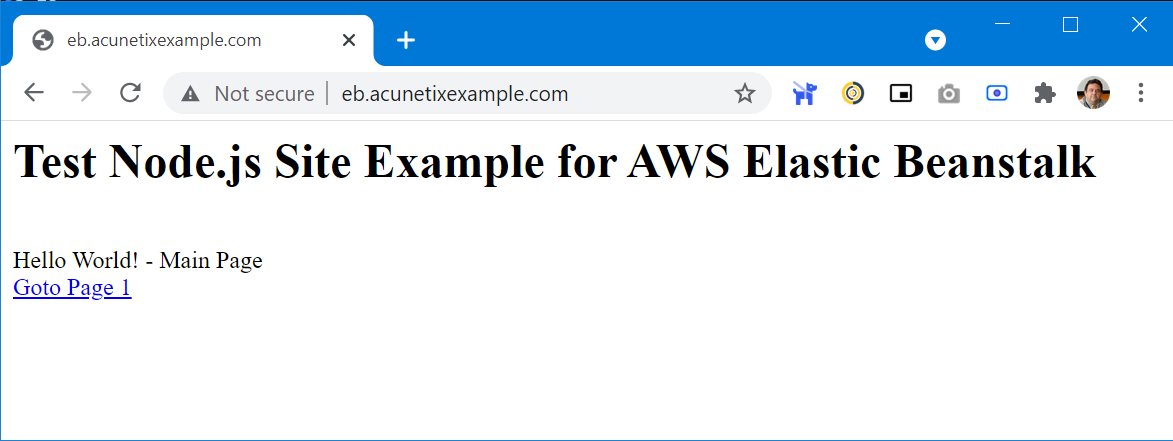
- Once the CNAME record has been added (giving time for DNS records to propagate), you can see the web application you have created by browsing to your URL (in this example
http://eb.acunetixexample.com):
Step 4: Test and scan your web application
- Point your browser to your web application, in this example
http://eb.acunetixexample.comto confirm it's running as intended. - Run a scan on your URL. The scan summary displays whether Invicti Shark is used for the scan.
Need help?
Invicti Support team is ready to provide you with technical help. Go to Help Center